Majority of javascript developers use AngularJs MVC pattern, because its offers architectural benefits over standard javascript.
It decouples the model and view which leads to effortless maintenance in the project.
Model
Model represents the current state of the application data.
Model is primarily concerned with business data.
Model consistently notifies its observers (e.g views) that a change has occurred so that views reacts accordingly.
For Example: Lets consider there is a model that holds the value for a dropdown list on the page. Once the model is updated it notifies the dropdown to show the new set of values.
View
View is a visual representation of current state of the model.
A view consistently observes the model and once the model notifies a change, it reacts accordingly.
View is a DOM element which interacts with the users.
Controller
In Angular, controller is a Javascript function which controls the models and views.
Controller has two parts i.e state ($scope variable) and behavior ($scope function).
Controller is attached to the DOM via the ng-controller directive.
Controller runs only once during the page load. After that a hook is created between View (DOM) and Model ($scope variable/ $scope function). Once the view is updated all the hooked functions for the respective controller are executed.
A page can have more than one controller. It can be associated to any DOM element like div,p,input,label.
Sample code for above output
<script src = "http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.14/angular.min.js">
</script>
<body ng-app="employeeApp">
<div ng-controller="pfController">
Please Enter Your Basic Pay : <input ng-model="basicAmount" type="text"/>
<p ng-bind="pf"></p>
<p ng-bind="epf"></p>
<p class="ng-cloak">{{ pfAmount() }}</p>
</div>
</body>
<script>
var employeeApp = angular.module("employeeApp",[]);
employeeApp.controller("pfController",function($scope){
/* scope varibales */
$scope.basicAmount = 0;$scope.pf='';$scope.epf='';
/* scope function - Below function will call when
you trying to change the value in basic Pay textbox */
$scope.pfAmount = function(){
$scope.pf = "PF Amount for Your Basic Pay : "+($scope.basicAmount*12)/100;
$scope.epf = "EPF Amount for Your Basic Pay : "+($scope.basicAmount*12)/100;
return "Above Calculation is 12% of Basic Pay";
};
});
</script>
ngApp
The first ngApp found in the document is used to define the root element to auto-bootstrap an application. ngapp is typically placed near the root element of the page like in the body or html tag.
ng-app executes at priority level 0.
ngInit
This directive is used to initialize the application data.
ng-init executes at priority level 450.
ngRepeat
This directive is used to iterate over the properties of an object.
ng-repeat executes at priority level 1000.
ngCloak
Generally ngcloak directives is used to avoid the flickering effect caused by the html template display.
All html elements (including their children) that are tagged with the ngCloak directive are hidden because ng-cloak have css rule embedded within angular.js and angular.min.js.When Angular encounters this directive during the compilation of the template it deletes the ngCloak css attribute, making the compiled element visible.
ng-cloak executes at priority level 0.
Example for ngApp,ngInit,ngRepeat,ngCloak
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.14/angular.min.js">
</script>
<div ng-app="initrepeatApp" ng-init="list = [1,2,3,4,5]">
<p>Iterate the list object </p>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="val in list">
<span ng-cloak>{{val}}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var initrepeatApp = angular.module("initrepeatApp",[]);
</script>
ngModel
ngModel binds the view to the model.
View can be any HTML controls (input, select, textarea).
Model can be any application data.
Keeps the state of the control (valid/invalid, dirty/pristine, touched/untouched, validation errors).
ng-model executes at priority level 1.
ngController
Controller is attached to the DOM via the ng-controller directive.
Controllers are used to set up the initial state of the $scope object or add method or behavior to the $scope object.
This directive creates new scope object for each controller.
ng-repeat executes at priority level 500.
ngBind
The ngbind attribute will continuously update the content of the specified HTML element with the value of a given expression.
ngbind directive is preferable than double curly markup because double curly markup is displayed by the browser in its raw state before angularjs complies it.So user can see flickering while the page is loading.Since ngBind is an element attribute, it makes the bindings invisible to the user while the page is loading.
ng-bind executes at priority level 0.
Example for ngModel,ngController,ngBind
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.14/angular.min.js">
</script>
<body ng-app="employeeApp">
<div ng-controller="pfController">
Please Enter Your Basic Pay : <input ng-model="basicAmount" type="text">
<p ng-bind="pfAmount()"></p>
</div>
</body>
<script>
var employeeApp = angular.module("employeeApp",[]);
employeeApp.controller("pfController",function($scope){
$scope.basicAmount = 0;
$scope.pfAmount = function(){
return "PF Amount for Your Basic Pay : "+($scope.basicAmount*12)/100;
};
});
</script>
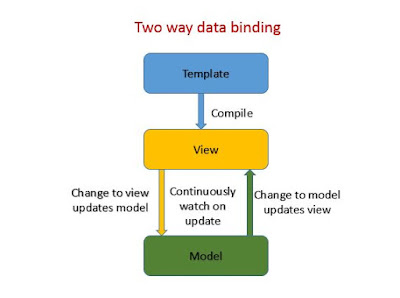
Two-way data-binding
Two way data binding means automatic synchronization of data between the model and view components.
Whenever the model changes,angular will cause the view to automatically update leading to no explicit DOM (Document Object Model) manipulation and vice versa.
Two way binding example in AngularJS
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.14/angular.min.js">
</script>
<div ng-app="">
Name: <input type="text" ng-model="name">
<p ng-bind="name"></p>
</div>
Explanation
The above code when a model(ng-model) variable is bound to a HTML element(input tag) that can both change and display the value of the variable.By using ng-bind to display the model.
Traditional Approach
In traditional approach we need to read user input and merge with the template to display the view on the screen. Everything we need to do explicitly.
Example in Jquery
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.3/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$("#name").keypress(function(){
$("#textboxvalue").text($("#name").val());
});
});
</script>
<html>
<body>
Name: <input id="name" type="text">
<p id="textboxvalue"></p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation
In Javascript or Jquery we need to do the explicit data binding by using DOM events like change,keypress etc.
In the above example value typed in the Name textbox is updated in paragraph (textboxvalue) by using keypress jquery function.
Key Features of AngularJS
Two-way data-binding
Two way data binding means automatic synchronization of data between the model and view components.
Whenever the model changes,angular will cause the view to automatically update leading to no explicit DOM (Document Object Model) manipulation and vice versa.
READ MORE
Minimal Code
AngularJS reduces the number of LOCs when compared to Javascript/JQuery.
Directives
At a high level, directives are markers on a DOM element (such as an attribute, element name, comment or CSS class)
which attach a special behavior to that DOM element (e.g. via event listeners), or even to transform the DOM element and its children.
Client side MVC framework
In Server side MVC framework, based on incoming client request the Controller existing at the server side retrieves the model and prepares the view which is sent back as a response to the client.
While in Angularjs the client gets the response from the server as JSON data. The client browser parses the data to generate the model, creates the view templates and renders the page.
Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection (DI) is a software design pattern that deals with how components get hold of their dependencies.
The Angular injector subsystem is responsible for creating components, resolving their dependencies, and providing them to other components as requested.
It reduces the load on the backend and helps to create a lighter application.
Filters
A filter formats the value of an expression or transform input to an output for display to the user. They can be used in view templates, controllers or services.It is easy to define your own filter.
Templating
Angular combines the template with information from the model and controller to render the dynamic view that a user sees in the browser.
Deep Linking
Deep linking allows you to encode the state of application in the URL so that it can be bookmarked.
The application can then be restored from the URL to the same state.
Reduce the network traffic when compare to use server side scripting language like jsp,asp.
REST.
Integration Test Runner.
Form Validation.
Localization.
Cross browser support and no dependency on any external libraries.
Disadvantages of AngularJS
Client must enable JavaScript in the browser.
Memory leak in JavaScript can even cause powerful system to slow down the browser.
AngularJS works well only from Internet Explorer 8.0 onwards and doesn't support any older versions.
Description
The application fails to release (or incorrectly releases) a system resource before it is made available for re-use.
This condition often occurs with resources such as database connections or file handles.
Most unreleased resource issues result in general software reliability problems,
but if an attacker can intentionally trigger a resource leak, it may be possible to launch a denial of service attack by depleting the resource pool.
Recommendations
When a resource is created or allocated, the developer is responsible for properly
releasing the resource as well as accounting for all potential paths of expiration or invalidation.
Ensure that all code paths properly release resources.
For More detail - Improper Resource Shutdown or Release
Sample issue Code
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ResourceRelease {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fin = null;
try{
fin = new FileInputStream("c:\\appv-instlog.txt");
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
Sample solution Code
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ResourceRelease {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fin = null;
try{
fin = new FileInputStream("c:\\appv-instlog.txt");
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(fin != null){
fin.close();
}
}
}
}
|
Overview
JVM will reclaim the unused object from heap memory for future use.Unused Object means no longer referenced by any part of your program pointer to that object.
To demonstrate unused object is reclaim by garbage collector by calling System.gc() function.System.gc() method provides just a "hint" to the JVM that garbage collection should run.
But It is not guaranteed!!
Parent object set to null
If an object holds reference of another object and when you set container object's reference null, child or contained object automatically becomes eligible for garbage collection.
Below Example - Garbage Collector will call when parent object references set to null
class EligibleParent{
protected void finalize(){
System.out.println("Parent Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector.");
}
}
class EligibleChild extends EligibleParent{
protected void finalize(){
System.out.println("Child Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector.");
}
}
public class EligibleParentNull {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EligibleParent obj = new EligibleChild();
obj = null;
System.gc();
}
}
|
Output
Child Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector.
|
Explanation
Above example System.gc() function is called after obj object set to null.Container object obj is null then contained object automatically becomes eligible for garbage collection.So the child
class finalize method is called.
Note : Output Order may change based on System.gc() function calling the finalize method.

Open Source Javascript Framework.
AngularJS is a structural framework for dynamic web application.
Perfect for Single Page Application (SPA).
It was developed in 2009 by Misko Hevery.
It is now officially supported by Google.
It extends HTML with new attributes.
There is no need of any server side Script like jsp,asp etc.
It can run anywhere where javascript can run because angularjs is completely written in javascript framework. Even supports many of the mobile browsers like Android,Chrome,safari etc.
It is entirely client side support framework.
It aims to simplify both the development and the testing of such applications by providing a framework for client-side model–view–controller (MVC)
and model–view–viewmodel (MVVM) architectures, along with components commonly used in rich Internet applications.
It lets you to use HTML as a template language and to extend
HTML syntax to elaborate your application components clearly and
succinctly.
Prerequisite for learning angularjs is HTML,CSS and Javascript.
AngularJS Offical Site
Overview
JVM will reclaim the unused object from heap memory for future use.Unused Object means no longer referenced by any part of your program pointer to that object.
To demonstrate unused object is reclaim by garbage collector by calling System.gc() function.System.gc() method provides just a "hint" to the JVM that garbage collection should run.
But It is not guaranteed!!
Instance lifetime or Scope of Object
Object References is vanishes at the end of the scope.No way to access the object, because the only reference to it is out of scope.
But still memory which is created by the object will Dangling in heap memory.So after out of scope instance is eligible for garbage collection.
Below Example - Garbage Collector will call when object references goes out of scope
public class EligibleScope {
protected void finalize(){
System.out.println("Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector:"+this);
}
public void createObject(){
EligibleScope obj1 = new EligibleScope();
System.out.println("obj1 address :"+obj1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EligibleScope obj = new EligibleScope();
System.out.println("Before called Garbage Collector");
System.out.println("obj address :"+obj);
obj.createObject();
System.gc();
System.out.println("After called Garbage Collector");
}
}
|
Output
Before called Garbage Collector
obj address :EligibleScope@dc8569
obj1 address :EligibleScope@1bab50a
After called Garbage Collector
Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector:EligibleScope@1bab50a
|
Explanation
Above example System.gc() function is called after the createObject method.obj1 object is created inside that function and its lifetime also over once that function gets over.
So that obj1 is reclaimed and it is called the finalize method.
Note : Output Order may change based on System.gc() function calling the finalize method.
Overview
JVM will reclaim the unused object from heap memory for future use.Unused Object means no longer referenced by any part of your program pointer to that object.
To demonstrate unused object is reclaim by garbage collector by calling System.gc() function.System.gc() method provides just a "hint" to the JVM that garbage collection should run.
But It is not guaranteed!!
Circular Nature
Object References is Circular Nature means initially Object is created on own memory address on heap memory and later more than one objects pointing to same memory address on heap memory.
Below Example - Garbage Collector will call when object references in circular nature occur
public class EligibleCircular {
protected void finalize(){
System.out.println("Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector:"+this);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EligibleCircular obj1 = new EligibleCircular();
EligibleCircular obj2 = new EligibleCircular();
System.out.println("Before Assinging obj2 to obj1 object");
System.out.println("obj1 = "+obj1);
System.out.println("obj2 = "+obj2);
obj1 = obj2;
System.gc();
System.out.println("After Assinging obj2 to obj1 object");
System.out.println("obj1 = "+obj1);
System.out.println("obj2 = "+obj2);
}
}
|
Output
Before Assinging obj2 to obj1 object
obj1 = EligibleCircular@1bab50a
obj2 = EligibleCircular@c3c749
After Assinging obj2 to obj1 object
obj1 = EligibleCircular@c3c749
Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector:EligibleCircular@1bab50a
obj2 = EligibleCircular@c3c749
|
Explanation
Above example System.gc() function is called after assigned obj2 to obj1.Both object is pointing the same address of obj2.Now obj1 memory address is Dangling pointer.
So the obj1 is reclaimed and it is called the finalize method.
Note : Output Order may change based on System.gc() function calling the finalize method.
Overview
JVM will reclaim the unused object from heap memory for future use.Unused Object means no longer referenced by any part of your program pointer to that object.
To demonstrate unused object is reclaim by garbage collector by calling System.gc() function.System.gc() method provides just a "hint" to the JVM that garbage collection should run.
But It is not guaranteed!!
Below Example - Garbage Collector is called before object assigning to null value
public class EligibleSetNull {
protected void finalize(){
System.out.println("Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EligibleSetNull obj1 = new EligibleSetNull();
System.out.println("Before Setting Null to Object.");
System.gc();
obj1 = null;
System.out.println("After Setting Null to Object.");
}
}
|
Output
Before Setting Null to Object.
After Setting Null to Object.
|
Explanation
Above example System.gc() function is called before setting the null value to object.So the object is not reclaimed and it is not called the finalize method.
Below Example - Garbage Collector is called After object assigning to null value
public class EligibleSetNull {
protected void finalize(){
System.out.println("Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EligibleSetNull obj1 = new EligibleSetNull();
System.out.println("Before Setting Null to Object.");
obj1 = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println("After Setting Null to Object.");
}
}
|
Output
Before Setting Null to Object.
After Setting Null to Object.
Unused Object is reclaim by Garbage Collector...
|
Explanation
Above example System.gc() function is called after setting the null value to object.So the object is reclaimed and it is called the finalize method.
Note : Output Order may change based on System.gc() function calling the finalize method.
Description
A function call contains an HTTP response splitting flaw. Writing unsanitized user-supplied input into an HTTP header allows an attacker to manipulate the HTTP response rendered by the browser, leading to cache poisoning and crosssite scripting attacks.
Recommendations
Avoid directly embedding user input in log files when possible. Sanitize user-supplied data used to construct log entries by using a safe logging mechanism such as the OWASP ESAPI Logger, which will automatically remove unexpected carriage returns and line feeds and can be onfigured to use HTML entity encoding for non-alphanumeric data. Only write custom blacklisting code when absolutely necessary. Always validate user-supplied input to ensure that it conforms to the expected format, using centralized data validation routines when possible.
For More detail - CWE-117: Improper Output Neutralization for Logs
Issue Code
strMessage=CLASSCONSTANTNAME+className+MESSAGENAME+message;
LOGGER.info(strMessage);
|
Fixed Code
strMessage=CLASSCONSTANTNAME+className+MESSAGENAME+message;
LOGGER.info(ESAPI.encoder().encodeForHTML(strMessage));
|
Explanation
Above Example Log information will come from anywhere in the application can contain CRLF.By using encodeForHTML method to Encode the user data for use in HTML using HTML entity encoding.
Note that the following characters: 00-08, 0B-0C, 0E-1F, and 7F-9F cannot be used in HTML.
Description
A function call contains an HTTP response splitting flaw. Writing unsanitized user-supplied input into an HTTP header allows an attacker to manipulate the HTTP response rendered by the browser, leading to cache poisoning and crosssite scripting attacks.
Recommendations
Remove unexpected carriage returns and line feeds from user-supplied data used to construct an HTTP response. Always validate user-supplied input to ensure that it conforms to the expected format, using centralized data validation routines when possible.
For More detail - CWE-113: Improper Neutralization of CRLF Sequences in HTTP Headers ('HTTP Response Splitting')
Issue Code
|
response.setHeader(headerKey,headerValue);
response.addHeader(headerKey, headerValue);
|
Fixed Code
|
DefaultHTTPUtilities httpUtilities = new DefaultHTTPUtilities();
httpUtilities.setHeader(headerKey,headerValue);
httpUtilities.addHeader(response, headerKey,headerValue);
|
Explanation
Above Example setting header value directly to response object.But HTTP header allows an attacker to manipulate the HTTP response rendered by the browser and it will vulnerability / Untrusted.
By using setHeader and addHeader function which is present in DefaultHTTPUtilities by ESAPI will avoid such an attack.
Description
A function call contains a CRLF Injection flaw. Writing unsanitized user-supplied input to an interface or external application that treats the CRLF (carriage return line feed) sequence as a delimiter to separate lines or records can result in that data being misinterpreted. FTP and SMTP are examples of protocols that treat CRLF as a delimiter when parsing commands.
Recommendations
Sanitize CRLF sequences from user-supplied input when the data is being passed to an entity that may incorrectly interpret it.
For More detail -
CWE-93: Improper Neutralization of CRLF Sequences ('CRLF Injection')
Issue Code
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress(validSenderStr.toString());
|
Fixed Code
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress
(ESAPI.encoder().encodeForHTML(validSenderStr.toString()));
|
Explanation
Above Example "validSenderStr" is input from anywhere in the application can contain CRLF.By using encodeForHTML method to Encode the user data for use in HTML using HTML entity encoding.
Note that the following characters: 00-08, 0B-0C, 0E-1F, and 7F-9F cannot be used in HTML.
Description
A web application accepts a user-controlled input that specifies a link to an external site, and uses that link to generate
a redirect.
Recommendations
Always validate user-supplied input to ensure that it conforms to the expected format, using centralized data validation routines when possible. Check the supplied URL against a whitelist of approved URLs or domains before redirecting.
For More detail - CWE-601: URL Redirection to Untrusted Site ('Open Redirect')
Issue Code
url = "/myapp/"+reqNo+"/view";
((HttpServletResponse)response).sendRedirect(url);
|
Fixed Code
DefaultHTTPUtilities utilities=new DefaultHTTPUtilities();
url = "/myapp/"+reqNo+"/view";
utilities.sendRedirect(url);
|
Explanation
Above Example "reqNo" value which is present in URL is used to redirect the request.But that value can be anything.So it will let redirect vulnerability.
By using ESAPI to avoid such a vulnerability.
|